|
Dr. Ilani has special interest in evaluation and treatment of thyroid disorders including thyroid hormone irregularities and thyroid nodule and cancer.
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned on this page, you may have thyroid irregularities and will need endocrine evaluation. If you have any thyroid nodule which is palpable or found incidentally by imaging, Dr, Ilani will evaluate your nodule with ultrasound and if needed will perform the fine needle aspiration of the thyroid nodule.However you will need a blood test for thyroid function test prior to any intervention. If the thyroid is overactive then thyroid scan (nuclear medicine imaging) should be performed for further evaluation of the nodule. Fine needle aspiration in our office is performed under ultrasound guidance to confirm correct needle placement and is done with thin needle as few passes will be performed for each nodule under local anesthesia. This is an out patient procedure and the patient will be able to continue usual daily activity after the procedure. In our office we are able to obtain a sample for genetic bio-markers related to thyroid cancer and reserve the sample to be available if the pathology result of the thyroid nodule aspiration is suspicious. Minority of thyroid nodules are cancerous but the diagnosis is important given early detection will provide cure of the thyroid cancer, however late detection will cause morbidity and may even cause mortality. 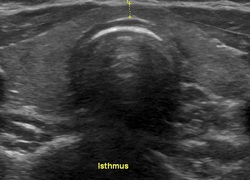
Thyroid ultrasound image
Transverse view Thyroid nodules are mostly asymptomatic but if they are very large, may cause compressive symptoms including difficulty swallowing and breathing.
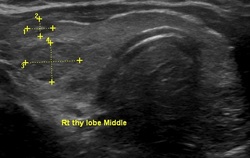
Thyroid Nodule
Transverse view A nodule may be cancerous if the lymph nodes under the jaw are swollen and if it grows quickly, feels hard, and causes pain. Cancerous nodules also tend to cause hoarseness or difficulty with swallowing or breathing.
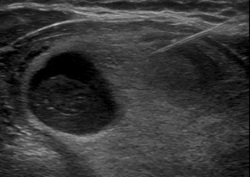
Fine Needle Aspiration of Thyroid Nodule
Thyroid scan is a nuclear medicine imaging which provides important information in a patient with thyroid nodule who's thyroid hormone test shows hyperthyroidism.
If you are looking for a thyroid doctor in Santa Monica or Torrance, contact us for additional information.
|
What is thyroid gland and what does it do in our body?
Thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck. This gland secretes thyroid hormones and they regulate the body energy level, oxygen consumption and heat production. Thyroid problems typically occur when thyroid releases too much or too little hormones. An overactive or underactive thyroid can lead to a wide range of health problems. Hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism, the result of an overactive thyroid, more commonly affects women between the ages of 20 and 40, but men can also develop this condition. The symptoms of this thyroid condition can be frightening. Symptoms
Graves' disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It occurs when the immune system produces antibodies that attack the thyroid gland, making it produce too much thyroid hormone. This condition happens often in people with a family history of thyroid disease. In some people with Graves' disease, one of the noticeable symptoms may be swelling behind the eyes, causing discomfort or increased tearing, or causing the eyes to bulge. Other causes of hyperthyroidism include the following:
caused by a virus. When the infection leaves, the condition improves. Lymphocytic thyroiditis Postpartum thyroiditis. These related autoimmune disorders cause a temporary painless inflammation of the gland. Thyroiditis leads to leakage of thyroid hormone from the inflamed gland, raising hormone levels in the bloodstream. Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism, which occurs when an underactive thyroid does not produce enough hormones, can be a dangerous condition if untreated. Instead of the bodily systems speeding up and overheating, they slow down in a variety of ways. This thyroid disease's symptoms include the following:
If you have severe hypothyroidism, a significant injury, infection, or exposure to cold or certain medications may trigger a life-threatening condition called myxedema coma. This condition may cause you to lose consciousness and to develop hypothermia, a life-threatening low body temperature. Causes of Hypothyroidism Hashimoto’s disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States. It occurs when the immune system produces antibodies that attack the thyroid gland, creating chronic inflammation that damages the gland and interferes with its ability to make enough thyroid hormone. It occurs more often in women than men, and tends to run in families. Hypothyroidism can be traced to several other conditions as well, including
Hypothyroidism is increasingly common as we age. Women over 50 should consider being screened for thyroid deficiency every few years. Hypothyroidism affects as many as 15 percent of women over 70 years of age. Thyroid Nodules and Cancer More than 90 percent of thyroid nodules are not harmful or cancerous. An individual may not be aware of the nodule until it starts to grow. A doctor may feel it, however, when examining the thyroid gland. To determine whether a nodule may be harmful and whether thyroid cancer treatment is needed, the doctor may perform any number of tests.
|